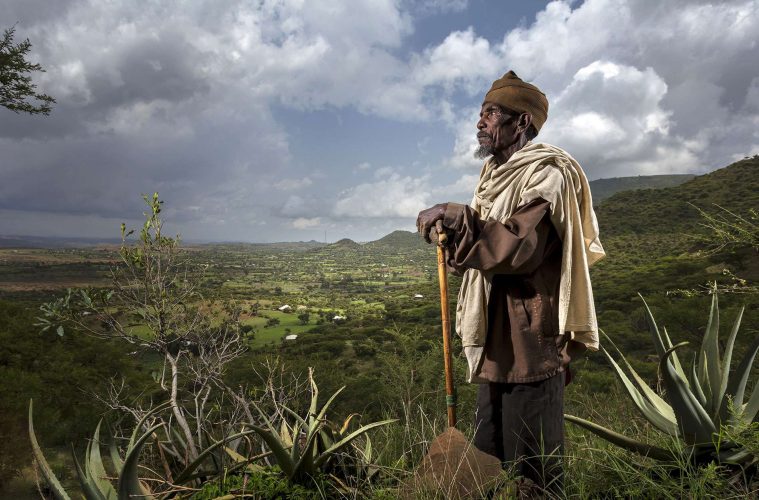
Ethiopia has been threatened for years by severe desertification affecting its agricultural lands. To counter this phenomenon, the Ethiopian government has put in place a comprehensive plan that has sustainable agriculture as its main pillar. These strategies are intended to increase soil restoration and conservation efforts.
Among the solutions presented to address this: soil management, restoration of degraded land, reforestation and agroforestry. The country is also focusing on improving incentive policies, through the establishment of international cooperation and the development of alternative livelihoods for local communities. In addition, it should be noted that the country’s forest cover has fallen sharply (from 40% at the beginning of the 20th century to only 15% today), hence the importance of focusing on sustainable and regenerative agriculture.
Located on the Horn of Africa, the country is experiencing a large loss of arable land that reaches about 30% throughout the national territory. In addition, more than 2 billion tonnes of fertile land is lost to erosion. This East African country aims to reduce the impact of desertification while ensuring sufficient income for local agricultural producers. The latter, who represent 85% of the population, depend heavily on rainwater, but are impacted by the arid climate that prevails in the country. Other initiatives launched by the country include The Great Green Wall, which aims to regenerate arable land degraded by erosion and desertification by 2030.